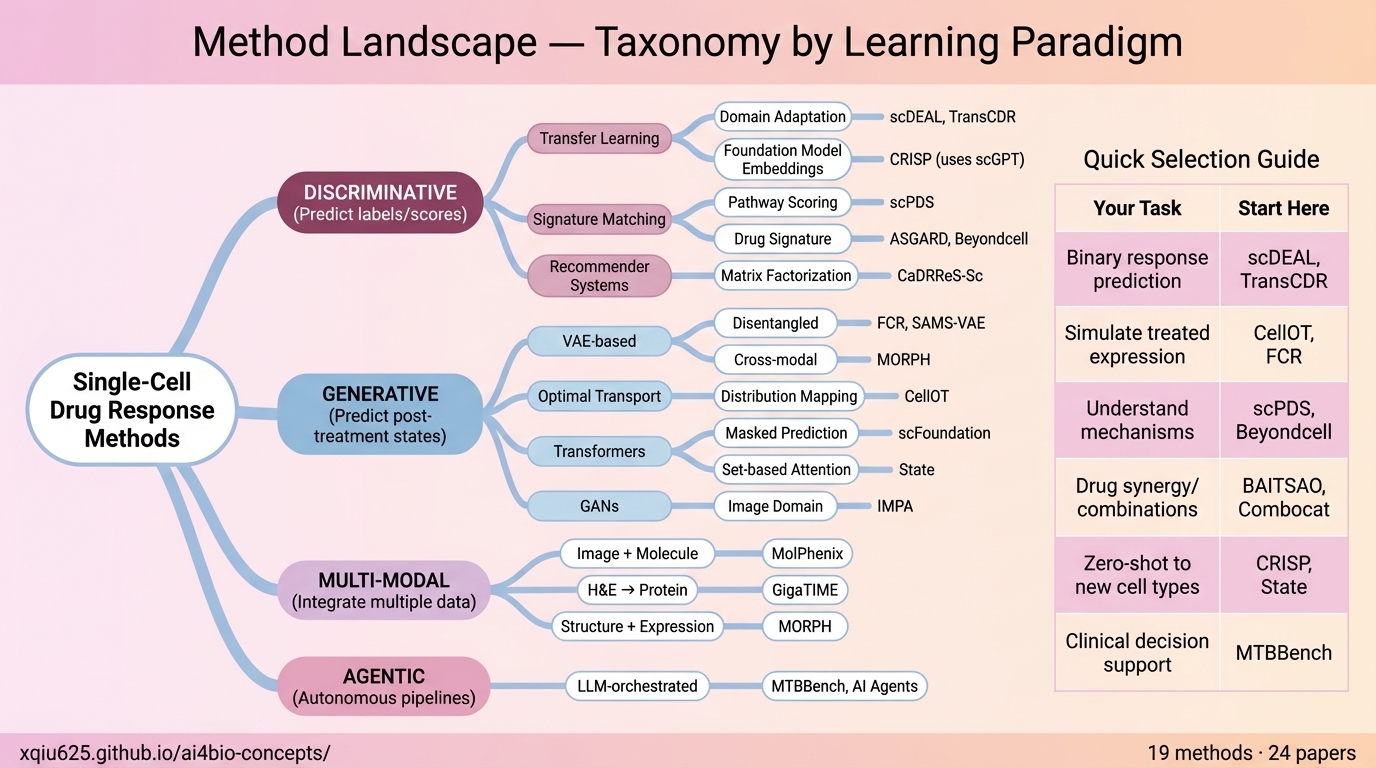
🧬 Single-Cell Drug Response Prediction
A User-Intent Guided Repository (2021-2025)
Navigating the landscape of computational pharmacology. Whether you need zero-shot prediction on unseen cell types, mechanistic pathway interpretation, or large-scale screening simulations, find the right AI tool for your specific biological question.
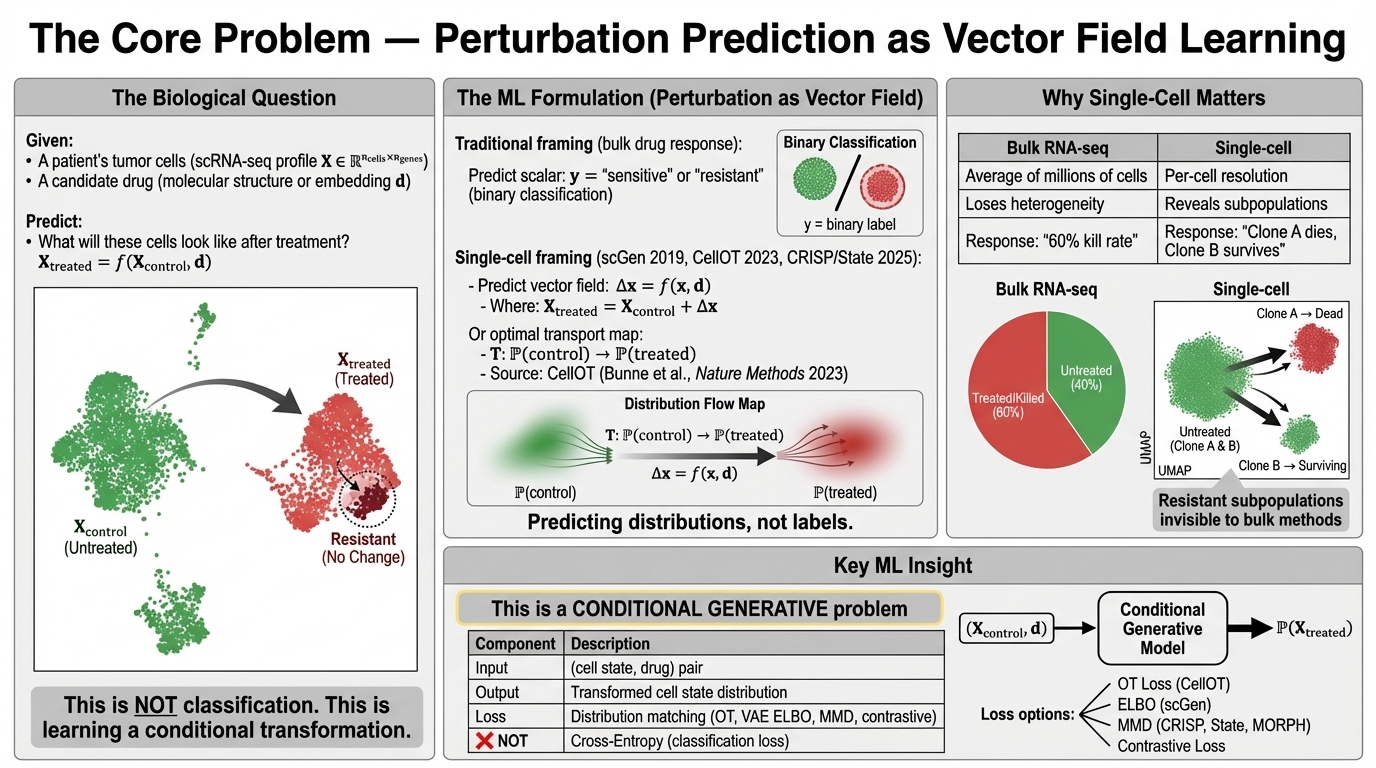
🎮 Concept: The Perturbation Vector
Before exploring specific tools, visualize the core challenge: moving a cell from a "Control" state to a "Treated" state. Modern AI methods (like CRISP) learn this vector field in high-dimensional space, while methods like State account for resistant subpopulations.
🚀 Foundation Models & Transfer Learning
CRISP
Uses embeddings from large foundation models (like scGPT) to enable zero-shot prediction of drug responses in unseen cell types. It maps perturbation effects across different cellular contexts.
State
A general-purpose Transformer trained on 100M+ cells. Uses set-based attention to model how entire populations of cells shift states under perturbation, rather than just single cells.
scFoundation
Large-scale pre-trained model on 50M+ cells using xTrimoGene architecture. Offers zero-shot capabilities for various downstream tasks, including drug response classification.
TransCDR
A deep learning model for cancer drug response prediction that transfers knowledge from bulk RNA-seq cell line data to single-cell patient data.
scDEAL
Deep transfer learning framework that integrates bulk and single-cell RNA-seq to predict cancer drug responses, harmonizing feature spaces between the two modalities.
🧪 Generative Perturbation (The "What If" Engines)
CellOT
Uses Neural Optimal Transport to learn a mapping between untreated and treated cell populations. Unlike standard style transfer, it respects the mathematical geometry of the cell state space.
FCR
Factorized Causal Representations. A VAE that disentangles cell identity from treatment effects, allowing for the generation of "counterfactual" single-cell states (e.g., "What if this specific cell had been treated?").
IMPA
Generative model for morphological perturbations. Uses style transfer GANs to predict how cell shape and structure change under chemical or genetic perturbation from microscopy images.
SAMS-VAE
Sparse Additive Mechanism Shift VAE. Models perturbation effects as sparse, additive shifts in latent space. Enables interpretable and composable predictions for drug combinations.
🧬 Mechanism & Interpretability
scPDS
Transforms gene expression into pathway activation scores before processing. Uses self-attention to capture interactions between biological pathways, offering high interpretability.
scGSDR
Gene semantics-based profiling. It integrates cellular states with signaling pathways to identify interpretable resistance phenotypes rather than just black-box probabilities.
scDrug+
Matrix factorization and SVM with molecular fingerprints show superior performance. Published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
🎯 Synergy, Prioritization & Screening
BAITSAO
Unified drug synergy model powered by GPT-3.5 embeddings. It predicts how two drugs will interact (synergy/antagonism) across hundreds of thousands of combinations.
scDrugPrio
An unbiased cell type-centric framework that prioritizes drugs based on single-cell disease signatures, helping identify candidates for repurposing.
scPharm
Identifies pharmacological subpopulations of single cells to reveal cell-type-specific vulnerabilities, aiding in precision oncology.
ASGARD
Single-cell Guided pipeline to Aid Repurposing of Drugs. Designed to connect cell-specific targets to existing drug databases for new indications.
CaDRReS-Sc
A matrix factorization-based recommender system (like Netflix for drugs) that predicts clone-specific therapeutic vulnerabilities.
DrugReflector
Deep learning ensemble trained on CMap signatures. Uses active reinforcement learning to iteratively refine hit discovery, achieving 13-17× improvement over random screening.
PBMF
Predictive Biomarker Modeling Framework uses contrastive learning to distinguish treatment-specific predictive biomarkers from prognostic markers, improving clinical trial patient selection.
📸 Multi-Modal & Morphological
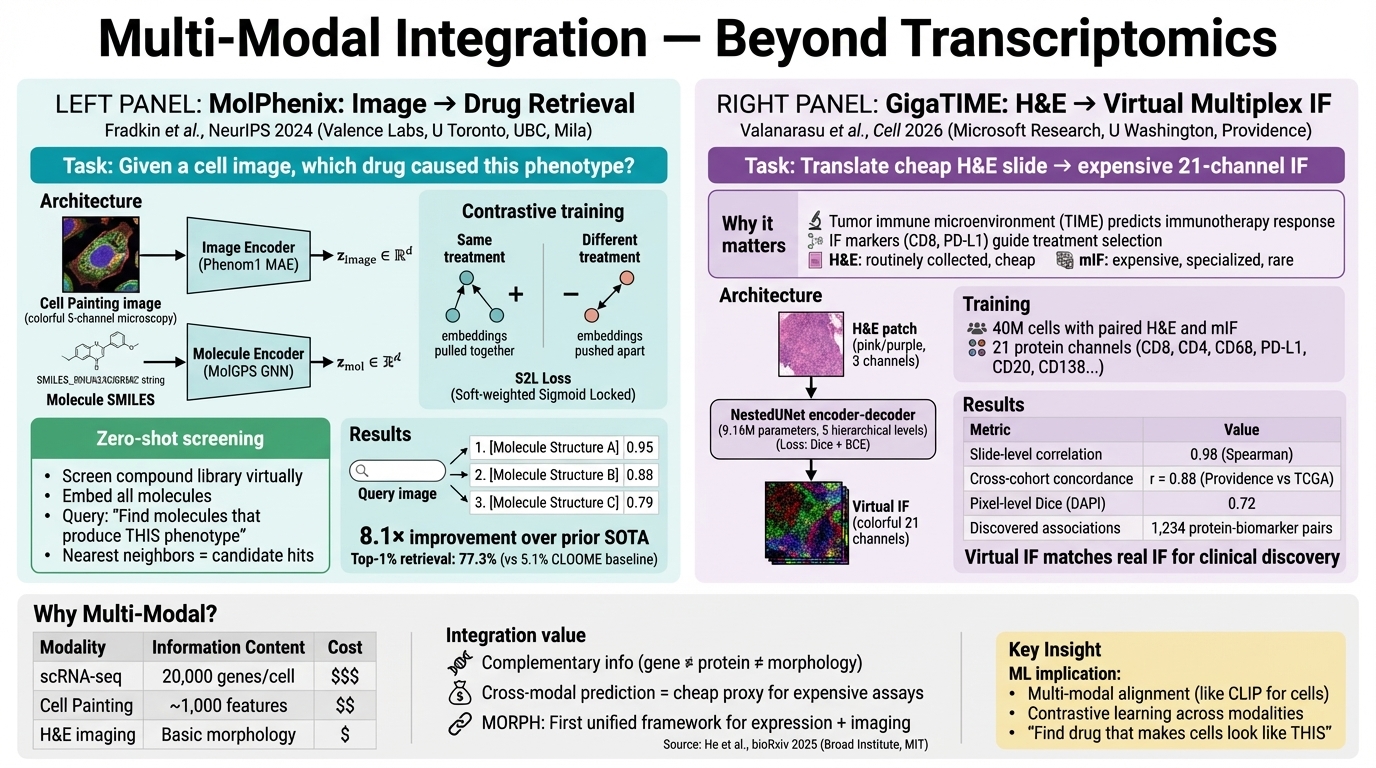
MolPhenix
Contrastive phenomolecular retrieval framework. It matches cell-painting images to molecular structures in a zero-shot manner, enabling virtual screening based on phenotype.
📚 Atlases, Databases & Benchmarks
Tahoe-100M
The largest single-cell perturbation atlas to date (95.6M cells). Profiles 379 drugs across 47 cancer cell lines with 1,138 drug-dose conditions. The "ImageNet" of perturbation biology.
ScDrugAct
A comprehensive database characterizing drug activity at the single-cell level. Useful for retrieving reference activity signatures for specific compounds.
TDC-2
Therapeutics Data Commons 2. The gold standard for benchmarking. Includes specific tasks for single-cell drug target identification and perturbation prediction.
🤖 AI Agents & Clinical Decision Support
Agentic AI in Drug Discovery
Comprehensive review of LLM-based agents with perception, computation, action, and memory tools. Documents case studies compressing drug discovery workflows from months to hours.
🧫 Experimental Platforms & Translational Tools
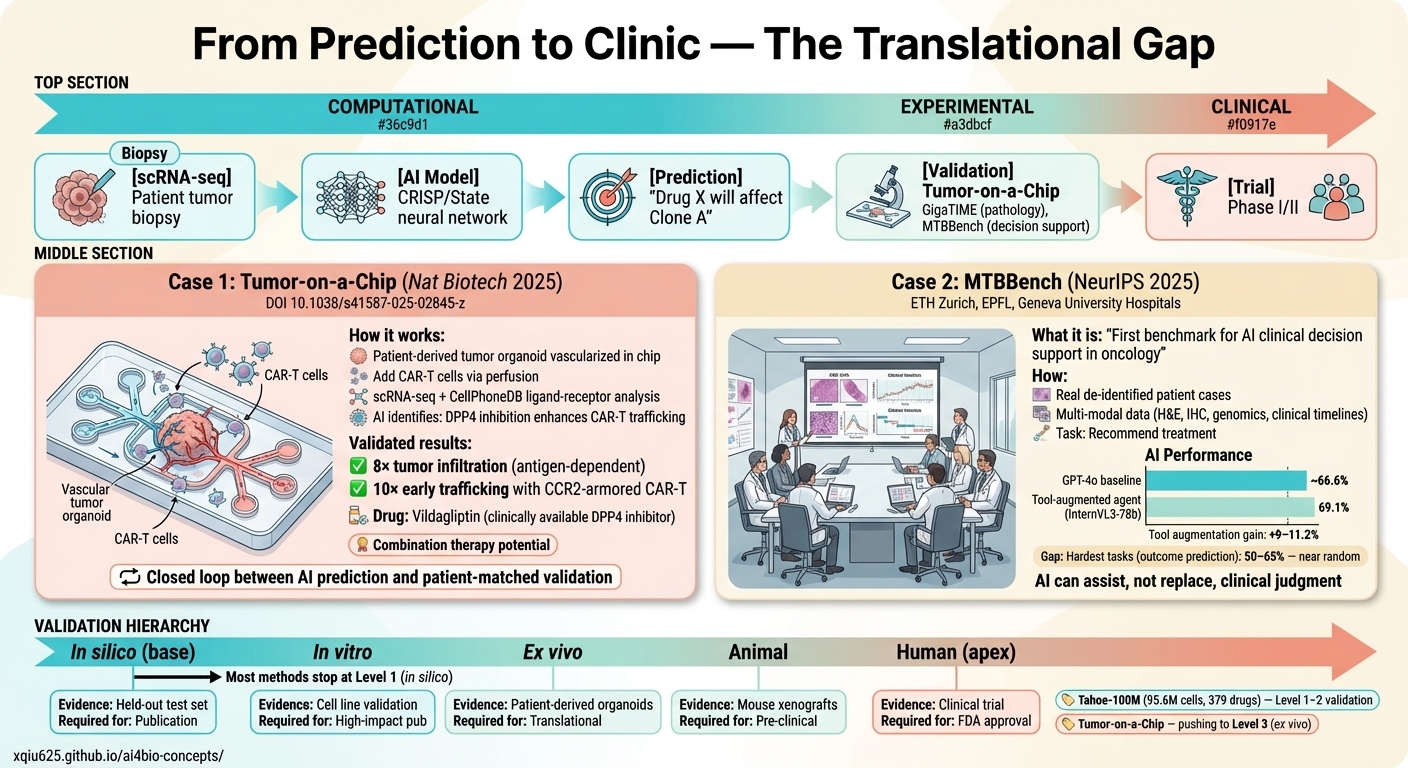
● Computational: scRNA-seq → AI Model (CRISP/State) → Prediction ("Drug X will affect Clone A")
● Experimental: Two validation case studies — Tumor-on-a-Chip (Nat Biotech 2025) enhances CAR-T trafficking 8× through DPP4 inhibition (vildagliptin) via CXCR3-CXCL10/11 axis; MTBBench (NeurIPS 2025) benchmarks AI clinical decision support showing tool-augmented agents reach 69.1% accuracy (+9–11.2% gain).
● Clinical: Phase I/II trials — the validation hierarchy from in silico (publication) through in vitro, ex vivo, animal models, to human trials (FDA approval).
Current frontier: Tahoe-100M (95.6M cells, 379 drugs) and Tumor-on-a-Chip pushing methods to Level 2–3 (ex vivo).
Tumor-on-a-Chip for CAR-T
Microengineered tumor-on-a-chip enabling vascularized human tumor explants and CAR-T cell perfusion. Identified DPP4/CXCR3 axis as combination therapy target via ligand-receptor analysis.